Webhook Authorisation
Introduction
Verifying the legitimacy of incoming webhook requests is crucial for webhook authentication. This process ensures requests come from trusted sources, protecting applications from unauthorised access and malicious activities. Without proper authentication, systems risk data breaches and exploitation.
This page gives an introduction to Webhooks and how they work, for a more in depth look at Webhooks, please go to our developers portal here.
What is a Webhook?
A webhook requires a sender (configured to recognise events) and a receiver (an application with an API). When an event occurs, the sender notifies the receiver. Webhooks are a simple way to subscribe to responses to application events.
Webhooks automatically notify you via an event if new information or data has been published.
Let’s take a look at an everyday example:
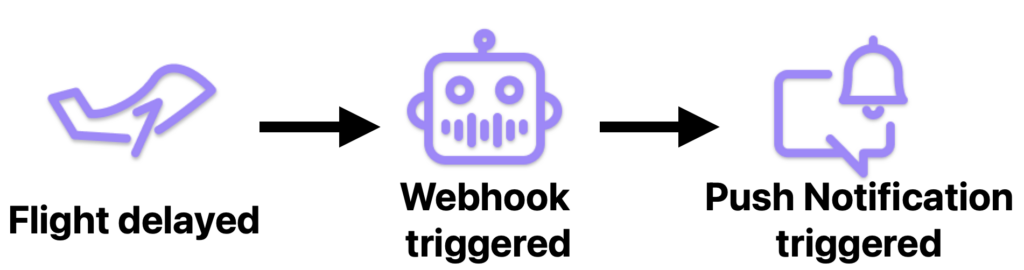
- You flight gets delayed.
- The Webhook is triggered because of the delay.
- Push notification is sent to you, advising of the delay.
Types of Webhooks
In this document, we will go through introductory examples of three Webhook Authentications that Esendex Connect provides. For more in-depth examples and information on these, you can access the developers portal here (add link when active).
Please be aware: Currently, you will only be able to have one form of Webhooks Authentication Method per account. If you try to send with more than one, you will get an error value stating that only one is allowed.
Basic Authentication
What is Basic Authentication?
Basic authentication is a straightforward HTTP authentication method that requires customers to submit their username and password in order to access an API endpoint. This approach is commonly used to secure API’s, ensuring that only authorised users can gain access to certain resources.
Journey
- When configuring basic authentication for a webhook, you have the option to supply either a username and password combination or the basic authentication token directly. This flexibility allows for easier integration and management of security credentials.
- When a username and password combination is provided, we generate an authentication token using the method of base64 encoding. (username:password). This approach adheres to the standard mechanism used in basic authentication.
- If the user does not adhere to the specified token creation guidelines, we provide an alternative option that allows them to set the token directly.
0Auth Verification Token (Bearer Token)
What is 0Auth?
In Auth0, the process of token authentication requires users to confirm their identity. Upon successful verification, Auth0 generates a unique token, such as an access token. This token provides users with access to secure resources, eliminating the need to repeatedly enter your credentials.
Journey
- Our platform needs permission to send information to our customer’s server. To do this, we need a special key to show that we have authorisation to do so.
- The customer’s platform will have an Authorisation Server that acts like a gatekeeper and will issue temporary access keys called Access Tokens.
- We would give our platform a public ID to help our customer’s server recognise who we are, we then prove the authenticity of this by providing a secret code (clientSecurityValue) that only we and our customer’s authorisation server will know.
- We then tell our platform where to go and get an Access Token (tokenUrl) from our customer, and what the secret code is that it will need to match with to pass through the customer’s gatekeeper (Authorisation Server).
- If the gatekeeper checks these and they are correct, then it will issue a temporary Access Token to our platform that will allow it to send information to the customer’s server with a timestamp that will expire after a set amount of time.
- Now, when our platform sends a webhook call to the customer’s server, it will include the Access Token as proof that it has been authorised. If this is accepted, then the information is successfully sent.
- A new Access Token must be used for each webhook call.
Custom Header (API Key)
What is Customer Header?
Custom header API key authentication is a method that utilises a unique key generated by the server. This key is included by clients in a custom HTTP header when making requests to access an API. This approach ensures secure access by verifying the identity of the client making the request.
Journey
- 1. API Key: An API key is a secret string that identifies the webhook sender.
- The creation of the API key will be generated by us for you (so relax and let us do the work).
- Your API key should be unique to you, Best practice is to generate a new API key for each webhook subscription.
- Your API key is sensitive information and will be treated as such.
- 2. Custom Header: The API key is sent through a custom HTTP header, which is defined by the webhook consumer.
- The name of the custom header is usually a unique identifier, such as “x-api-key” or “api-key”.
- Using HTTPS for webhook communication is recommended to secure the API key and other data in transit.
- 3. Webhook Request: When the webhook is triggered, the producer of the webhook (Esendex Connect) includes a custom header with the API key in the request.
- The webhook consumer must be configured to recognise the custom header and its related API key.
- 4. Authentication: The webhook consumer checks for the presence and validity of the custom header containing the API key. If the header is included and the API key is correct, the webhook request is deemed authentic.
- -API key will be 32 characters, case sensitive and alphanumeric
- 5. Validation: The webhook consumer (the user, i.e. you) validates the webhook request using the API key to decide if it should be authenticated.
Example
Assume you have an API key, “MY_ESENDEX_CONNECT_KEY,” and you want to use it in a custom header called “x-my-titan-key.” The webhook request should include this header:
x-titan-app-key: ESENDEX_ CONNECT_API_KEY
The webhook consumer must validate that this header exists and that the value “MY_ESENDEX_CONNECT_KEY” corresponds to a valid API key.
You can get a more in depth look at Webhook in our developers portal here.